TECHNOLOGY SEED
- Technology Platforms
Novel Helper Lipids for Enhanced mRNA Delivery
Novel helper lipids interact with phosphatidylcholine, facilitating phase transitions to enhance endosomal escape and boost mRNA delivery
Source: Dr_Microbe, stock.adobe.com/uk/519547367, stock.adobe.com
Background
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are essential delivery systems for RNA therapeutics, such as mRNA vaccines and protein replacement therapies. However, their efficacy is significantly limited by inefficient endosomal escape, typically under 10%. Current helper lipids like DSPC and DOPE have limitations in promoting endosomal fusion. To address this, the research team developed two novel helper lipids—zTOT and DOPE-Cx—that are engineered to induce non-lamellar (cubic) phases and enhance the cytosolic delivery of mRNA.
Technology Overview
Hokkaido University’s new helper lipids interact with phosphatidylcholine (PC) in endosomal membranes and form ion pairs that facilitate lipid phase transitions to non-lamellar cubic phases. This phase transition lowers the energetic barrier for membrane fusion, resulting in enhanced endosomal escape and mRNA delivery.
Structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies show that DOPE-Cx lipids with short hydrophobic chains (C6-C10) or specific branched side chains exhibit optimal cubic phase formation and gene expression. DOPE-C8 and DOPE-C6_β2 were particularly effective, showing a marked increase in liver gene expression in vivo compared to DSPC or DOPE.
The lipids are compatible with various ionizable lipids (e.g., CL4F6, ALC-0315) and have improved mRNA expressions by changing our new helper lipids from conventional helper lipids. They also demonstrate high encapsulation efficiency, low hemolytic activity at physiological pH, and rapid degradation in vivo, mitigating long-term toxicity concerns.
Further details:
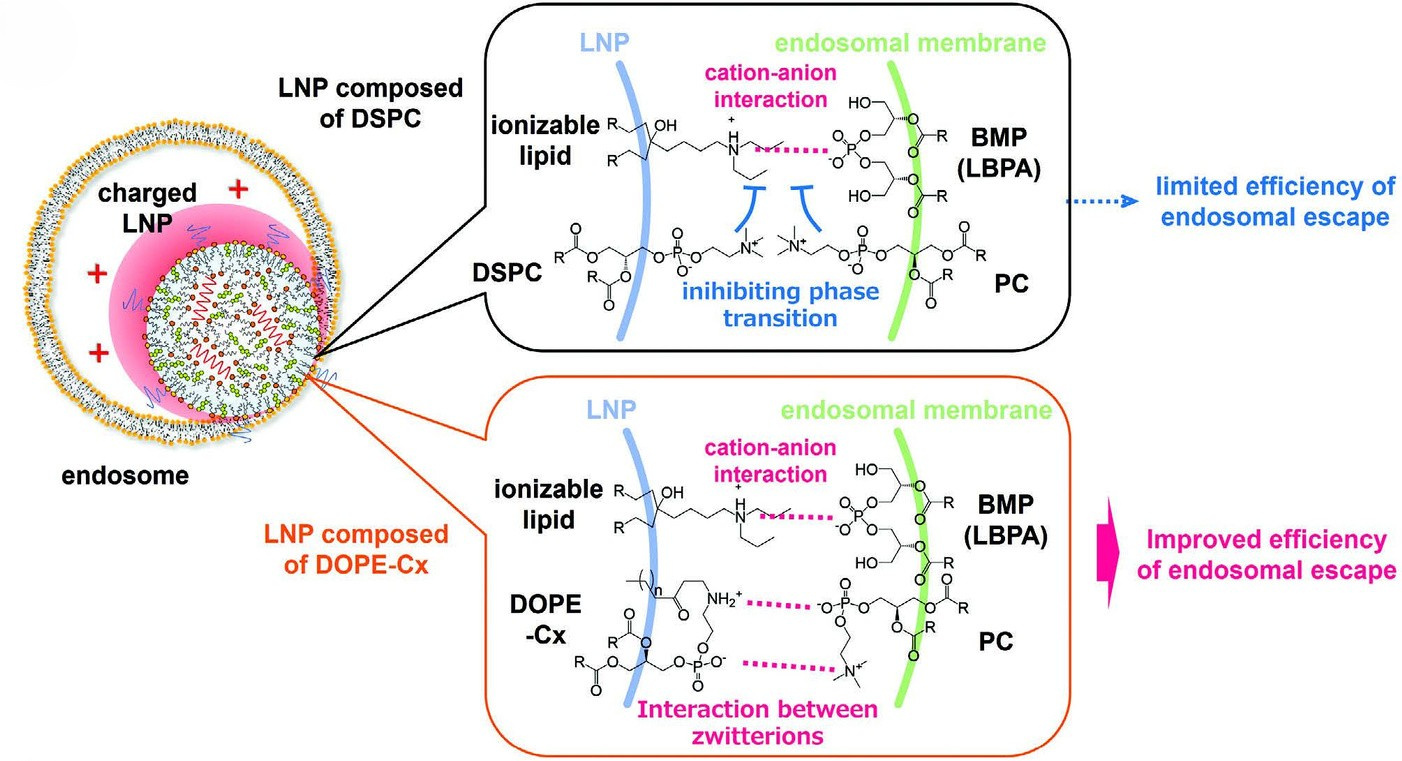
figure 1.
Benefits
- Significantly improves functional mRNA delivery via endosomal escape enhancement
- Induces cubic (Q) lipid phases, facilitating membrane fusion
- Compatible with existing LNP platforms and multiple ionizable lipids
- Rapid biodegradation reduces toxicity risk
- Tailorable via structural variations for optimal delivery performance
Applications
- mRNA vaccines (e.g., for infectious diseases like COVID-19)
- Protein replacement therapies
- Gene therapies using siRNA or plasmid DNA
- Oncology therapeutics
- Delivery systems targeting liver and other organs
Opportunity
Hokkaido University are seeking partners interested in using our novel helper lipids in the LNP formulations to improve RNA delivery efficiency. Potential partnerships may involve joint research, material evaluation under MTA, and subsequent licensing.
Link
inpart
Novel Helper Lipids for Enhanced mRNA Delivery (Technology) | Inpart