TECHNOLOGY SEED
- Technology Platforms
Novel RNA Therapeutic Delivery to Hepatic Stellate Cells via PDGF-Mediated Uptake for Liver Fibrosis Therapy
Two complementary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platforms for PDGF receptor beta (PDGFRβ)-mediated delivery of RNA therapeutics to aHSCs
Source: kanruthai, https://stock.adobe.com/uk/1630178398, stock.adobe.com
Background
Liver fibrosis is a chronic and potentially life-threatening condition caused by continuous liver damage, often progressing to cirrhosis and liver cancer. The primary drivers of fibrosis are activated hepatic stellate cells (aHSCs), which deposit excess extracellular matrix (ECM) in response to chronic injury. Recent advances in RNA-based therapies offer promising approaches, but targeted delivery to aHSCs remains a key hurdle due to their low frequency, fibrotic microenvironment, and the complexity of selective uptake. A solution that enables efficient, cell-specific delivery of both siRNA and mRNA payloads is essential for developing anti-fibrotic therapies.
Technology Overview
Hokkaido University presents two complementary lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platforms for PDGF receptor beta (PDGFRβ)-mediated delivery of RNA therapeutics—siRNA and mRNA—to aHSCs. These systems Hokkaido University developed use pH-sensitive lipids screened for optimal endosomal escape and formulated via a microfluidic production method (iLiNP). The mRNA platform, centered on the lipid CL15A6, demonstrated high encapsulation efficiency and efficient in vivo mRNA expression in fibrotic livers. Meanwhile, the siRNA platform utilized LNPs containing SS-cleavable and pH-activated lipid-like materials (ssPalmE-DP/LNPs), enabling gene silencing of fibrogenic targets such as HSP47 with minimal off-target expression.
Both platforms rely on a PDGF-dependent uptake mechanism via PDGFRβ, which is selectively overexpressed on aHSCs. This receptor-mediated, clathrin-dependent endocytosis allows for efficient, ligand-free targeting of aHSCs in vivo.
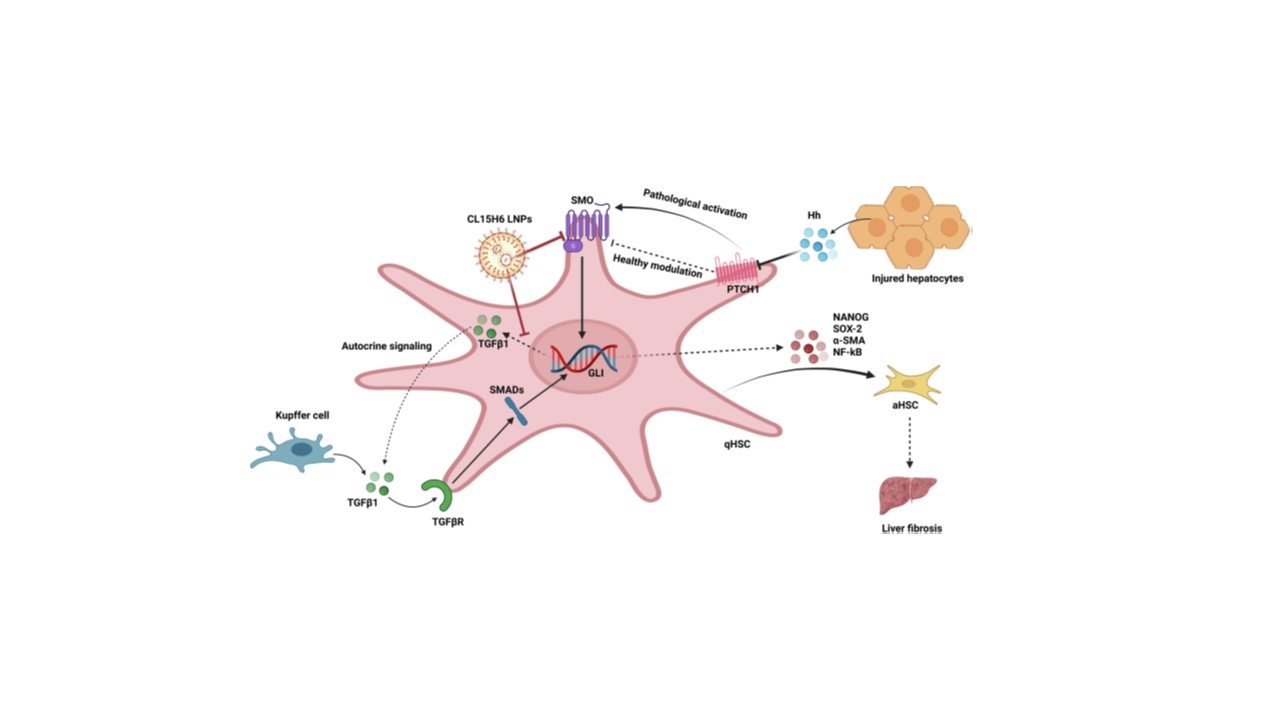
figure 1. Schematic of CL15A6 LNP and ssPalmE-DP/LNP uptake via PDGFRβ on aHSCs.
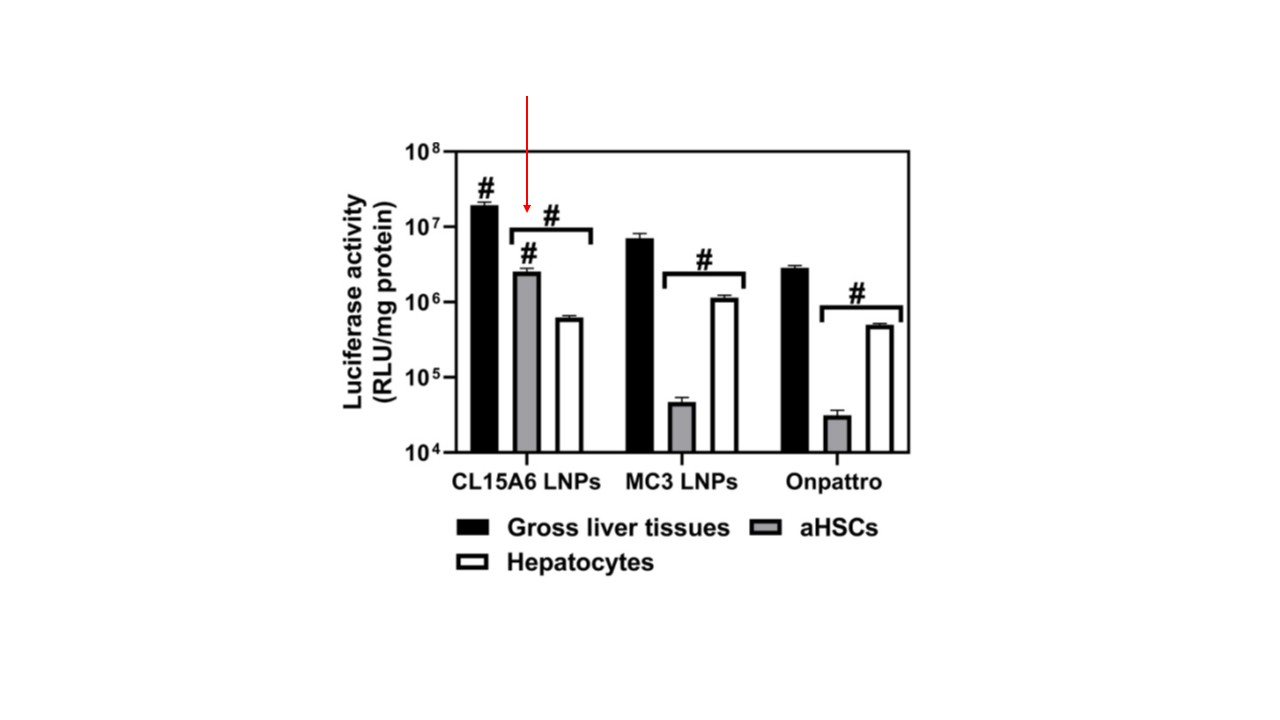
figure 2. Comparison of the functional delivery efficiency of FLuc mRNA to gross liver tissues, aHSCs, or hepatocytes 24 h post intravenous administration of the optimized CL15A6 LNPs, MC3 LNPs.
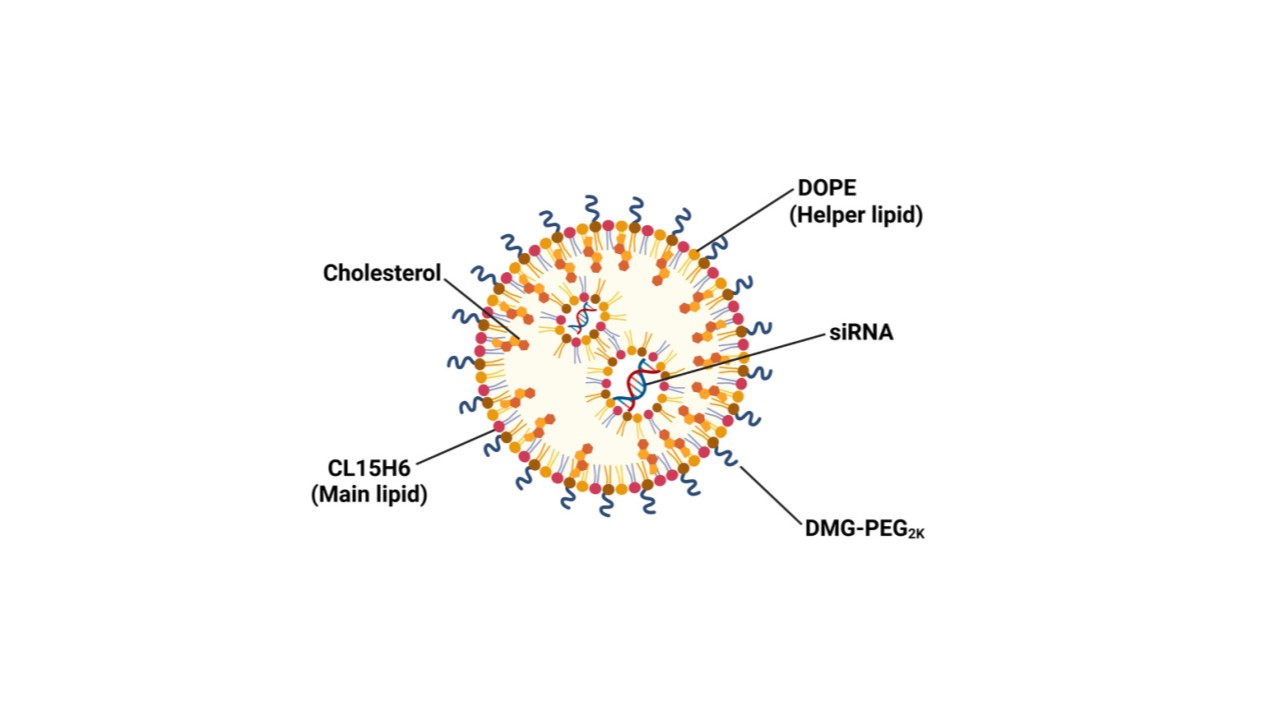
figure 3. The composition and characteristics of the optimized siRNA-loaded CL15H6 LNPs.
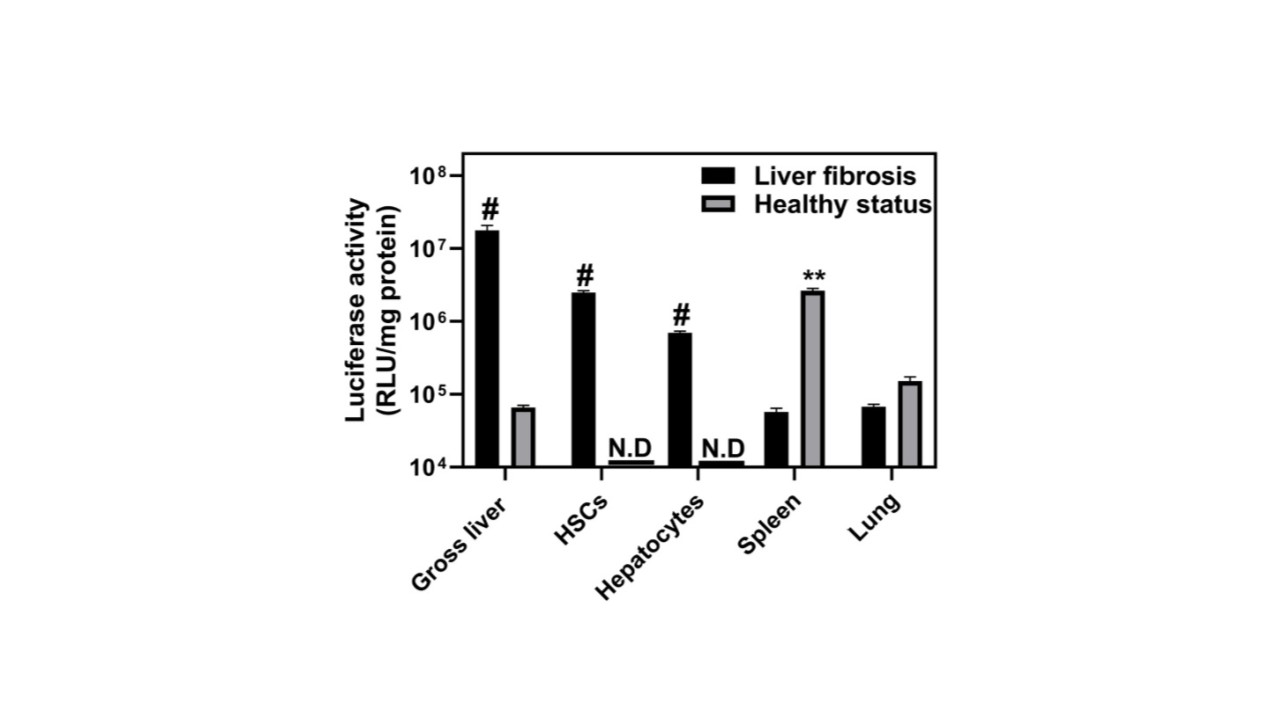
figure 4. Comparison of the functional delivery efficiency of FLuc mRNA by CL15A6 LNPs in healthy mice versus those undergoing liver fibrosis.
Benefits
- Selective delivery via PDGFRβ-mediated endocytosis enhances targeting specificity.
- Enables delivery of both mRNA (for protein expression) and siRNA (for gene silencing).
- Ligand-free design supports scalability and simplifies formulation.
- Demonstrated in vivo efficacy in fibrotic mouse models.
- Minimal off-target expression or immune stimulation observed.
Applications
- Dual gene therapy for liver fibrosis: knockdown of profibrotic genes and delivery of therapeutic proteins.
- Adaptable to other PDGFRβ-expressing fibrotic or inflammatory conditions.
- Platform technologies for RNA delivery and liver disease research.
Opportunity
Hokkaido University are seeking industry collaborators and development partners to advance these PDGFRβ-targeted RNA delivery platforms for liver fibrosis into preclinical and clinical applications. Opportunities exist for co-development, licensing, and translational funding partnerships.
Link
inpart
Contact